
AJAX Introduction
Junghoo Cho
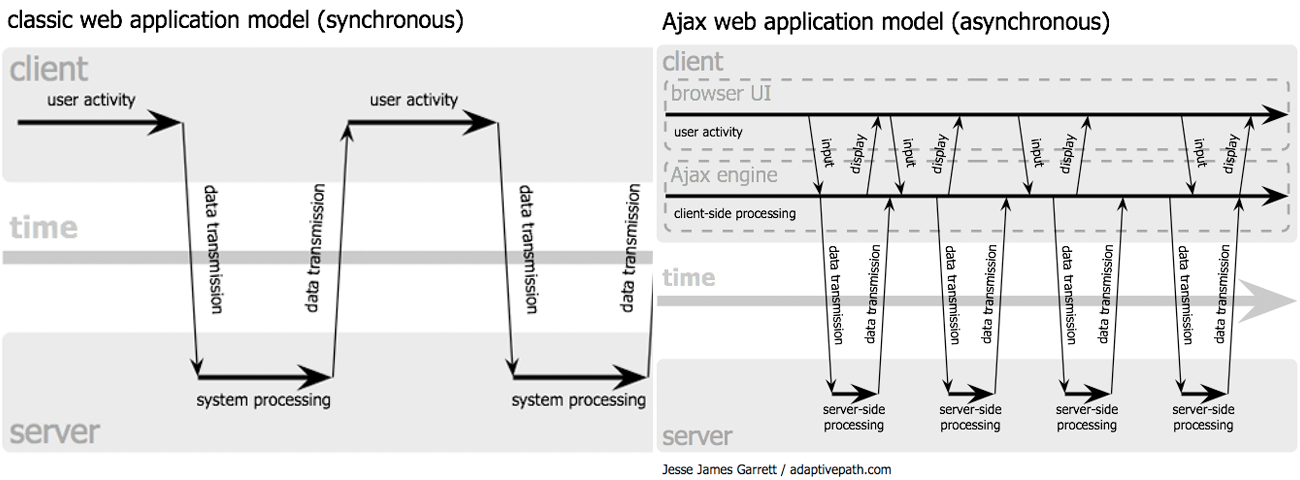
Traditional vs AJAX (1)
- Traditional
- Form-based input
- Press “submit” button and wait until the entire page reloads
- Constant interruptions and significant delay
- AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)
- Immediate, “in-place” update of page content
- More “desktop-application”-like feel
Traditional vs AJAX (2)
Our AJAX Demo
- Simple AJAX Example
- Q: What should the browser do for the demo?
- Q: How is the program execution determined?
- Event-driven
- Control flow is driven by “events”
- Callback function
- Map events to actions. “If this event happens, then call this function”
- Q: What mechanisms are needed to support this app?
- Dynamic in-place page update mechanism
AJAX Building Blocks
- JavaScript: The programming language for the Web
- Allows running complex code inside a browser
- Document Object Model (DOM)
- Tree-based model of HTML document
- JavaScript manipulates DOM to dynamically change page
- JavaScript monitors “events” on DOM and take actions
- Asynchronous communication mechanism with server
fetch (and old XMLHTTPRequest): more on this later
